
What are 3D and 3D Movies?
3D (three-dimensional) means something that has width, height and depth (length). It is a concept relative to 2D (something only has width and height).
3D movies refer to the motion pictures adding stereoscopic vision.
What are 3D and 3D Movies?
3D movies mainly make use of human eyes' visual angle difference and convergence to produce stereoscopic effect.
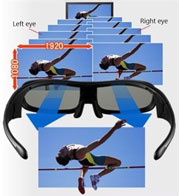
Human visual can tell far or near distance because of the distance between two eyes. There are about five centimeters between left eye and right eye and two eyes' visual angle are different when seeing something except when starring at the front. Although the difference is small, after being transferred to brain via retina, our brain can use this small difference to produce far or near depth thus to produce stereoscopic effect. We call this principal "Polarizing Theory".
According to this principal, if we make two separate images of a same picture from two eyes' visual angle difference, and show these two separate images simultaneously – one to each eye, we can feel the stereoscopic effect of the image with the help of special projection hardware and/or eyewear like 3D glasses.
General 3D Movies Modes
Common 3D film modes include Anaglyph and Split Screen.
1. Anaglyph
Anaglyph refers to color filtered 3D pictures including amber/blue, red/green, red/blue and red/cyan. Among these 3D image flavors, red/cyan is the most popular one. Anaglyph 3D is the earliest method to present theatrical 3D, as it requires less specialized hardware.
According to Wikipedia, "In an anaglyph, the two images are superimposed in an additive light setting through two filters, one red and one cyan. In a subtractive light setting, the two images are printed in the same complementary colors on white paper. Glasses with colored filters in each eye separate the appropriate images by canceling the filter color out and rendering the complementary color black."
To watch the Anaglyph 3D video, what you need is just a pair of archetypical 3D glasses. And you can play the 3D video on common TV, computer monitors, and even the common portable devices.

2. Split Screen 3D
Side by Side 3D
In 3D Side by Side, one frame consists of two halves on the left and right, with the entire frame for the left eye scaled down horizontally to fit the left-half of the frame, and the entire frame for the right eye scaled down horizontally to fit the right side of the frame.
When TV receives this 3D Side by Side signal, it splits each frame to extract the frame for each eye, and then rescales these individual frames to a full HD resolution using upscaling algorithms. It then displays these upscaled individual frames alternately in a frame-sequential manner.
Let's take a 720p (resolution of 1280*720) source video as an example to see the difference between Side by Side (Half-width) and Side by Side (Full)
If you choose the Side by Side (Half-width), the output video frame for the left/right eye will be at a 640*720 resolution, and the resolution of the output video will be 1280*720.
If you choose the Side by Side (Full), the output video frame for the left/right eye will be at a 1280*720 resolution, which means the resolution of the output video will be 2560*720. So before you choose the Side by Side (Full) as the output 3D mode, you should check whether the device supports the output video resolution first.

Side by Side (Half-width)

Side by Side (Full)
Top and Bottom 3D
In the Top and Bottom 3D mode, one video frame is divided into two sub-frames, the upper one consisting of the sub-frame meant for the left eye and the lower sub-frame meant for the right eye.
The difference between Top and Bottom (Half-height) and Top and Bottom (Full) can be largely understood the same as the difference between the two Side by Side modes. The output Top and Bottom (Half-height) 3D video will keep the resolution of the source video, and the output Top and Bottom (Full) will double the vertical resolution of the original video.
When playing a Side by Side 3D or Top and Bottom video, a 3D PC or 3D TV and the assorted 3D glasses are necessary. But the visual effect of Side by Side 3D and Top and Bottom 3D video is much better compared to that of Anaglyph 3D video.

Top and Bottom (Half-height)

Top and Bottom (Full)
3D TV and 3D Glasses
3D TV is television that conveys depth perception to the viewer. 3D display technologies include two types: With lenses (anaglyphic 3D system, active shutter 3D system and polarization 3D system) and without lenses (glasses-free 3D system). To what a 3D TV with lenses, you have to wear a 3D glasses, which refer to any form of stereoscopic viewers.
1. With lenses
Anaglyphic 3D – Anaglyphic 3D uses passive color filtered 3D glasses. This technique has the longest history and the 3D imaging principle is simple. The cost is quite low – 3D glasses cost is only a few dollars. However, the 3D effect is the worst and this technology is not widely used.
Active Shutter 3D – Active Shutter 3D uses rechargeable 3D glasses. The lenses are actually two LCD screens. The current controls two lenses transmitting light alternatively and in the meantime, the 3D TV display twinkles alternatively in keeping with lenses. In this way, our eyes can see two separate images and 3D images are produced in our brain.
Active shutter 3D TVs include: Samsung H6400, Samsung H7150, Samsung H8000, Samsung HU8550, Samsung HU9000, Sony W800B, Sony W850B, Sony X900B, Sony X950B, etc.

Polarization 3D – Polarization 3D uses 3D glasses with liquid crystal membrane like sunglasses. The TV screen has an outer membrane matched with the 3D glasses and when watching 3D videos, the outer membrane makes separate images filtered through left and right lens and then 3D effect is produced in our brain.

Polarization 3D TVs include: LG LB7100, LG LB7200, Sony W950B, Sony X850B, etc.

2. Without lenses
Glasses-free 3D – When watching glasses-free 3D, we need to keep certain distance with the display device (3D effect has big relationship with viewing angles). The 3D effect is worse compared with active shutter 3D and polarization 3D.
Glasses-free 3D TVs include: Samsung 55-inch Glasses-Free 3D UHD TV, Sharp 85-inch 8K Glasses-Free 3D TV, Toshiba 56-inch Glasses-Free 3D TV, Haier Glasses-Free 3D TV, Leyard 110-inch Glasses-Free 3D TV, etc.

Convert 2D to 3D
Sometimes you only have 2D videos but are eager to experience 3D effect. You may ask is there a way to achieve so except buying another 3D video? The answer is yes. You can convert 2D to 3D video with 2D to 3D software. Then you are able to enjoy your converted 3D videos on your 3D TV, 3D video player or other 3D devices.




